

The most simple definition of Aquaponics is the combination of aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (the soil-less growing of plants) that grows fish and plants together in one integrated system. The fish waste provides an organic food source for the plants, and the plants naturally filter the water for the fish.
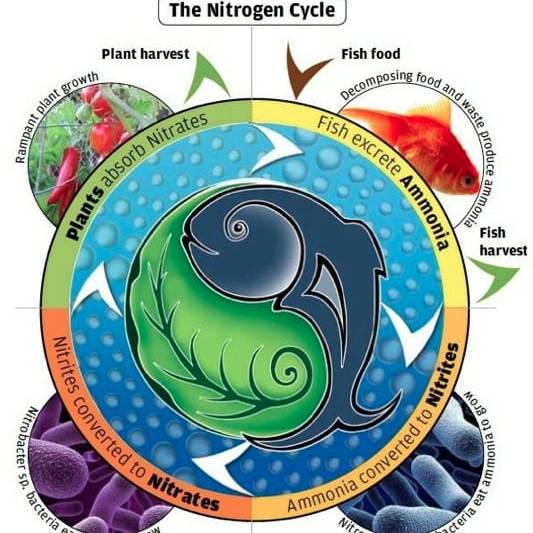
The third participants are microbes (nitrifying bacteria). These bacteria convert ammonia from the fish waste first into nitrites, and then into nitrates. Nitrates are the form of nitrogen that plants can uptake and use to grow. Solid fish waste is turned into vermicompost that also acts as food for the plants.
In combining both hydroponic and aquaculture systems, aquaponics capitalizes on their benefits, and eliminates the drawbacks of each.
Natural and Sustainable
Aquaponics is a completely natural process that mimics all lakes, ponds, rivers and waterways on Earth. The only input into an aquaponics system is fish food. The fish eat the food and excrete waste, which is converted by beneficial bacteria to nutrients that the plants can use. In consuming these nutrients, the plants help to purify the water. You cannot use herbicides, pesticides or other harsh chemicals in an aquaponics system, making the fish and plants healthful and safe to eat.
